Comprehensive Guide to Controllable Pitch Propeller (CPP) Systems and OD Box
1. Introduction to CPP Technology
Controllable Pitch Propeller (CPP) systems represent a sophisticated marine propulsion solution that has revolutionized ship maneuverability and operational efficiency since their introduction in the 1930s. Today, approximately 60% of modern vessels utilize CPP technology due to its superior control capabilities compared to fixed-pitch propellers.
Key Advantages:
- Enhanced maneuverability in port operations
- Optimal fuel efficiency across varying load conditions
- Reduced mechanical stress on propulsion components
- Quick response time for emergency maneuvers
2. Core System Components
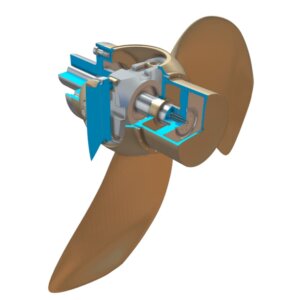
2.1 Mechanical Assembly
- Propeller Hub: Stainless steel construction with corrosion-resistant coatings
- Blade Mechanism: 4-6 bronze or stainless steel blades with ±35° pitch range
- Hydraulic Cylinder: Internal hub mechanism operating at 150 bar working pressure
2.2 Hydraulic System
Hydraulic Pumps:
- Primary Type: Axial piston pumps (Bosch Rexroth, Kawasaki)
- Flow rate: 30-150 L/min
- Pressure rating: 140-210 bar
- Volumetric efficiency: >95%
- Backup Systems: Gear pumps for auxiliary functions
Hydraulic Fluid Specifications:
Recommended brands: Shell Tellus S2 MX, Mobil DTE 10 Excel
| Parameter | Requirement | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity Grade | ISO VG 46/68 | ISO 3448 |
| Viscosity @40°C | 41-50 mm²/s | ASTM D445 |
| Viscosity Index | >120 | ASTM D2270 |
| Acid Number | <0.5 mg KOH/g | ASTM D664 |
| Water Content | <200 ppm | ASTM D6304 |
Control Valves:
- Proportional Valves (Moog, Bosch Rexroth):
- Accuracy: ±0.1% full scale
- Response time: <50ms
- Pressure rating: 280-350 bar
- Safety Valves:
- Pressure relief valves (110% working pressure)
- Emergency stop valves (ESD activated)
- Counterbalance valves
2.3 Electronic Control System
- PLC-based control architecture
- LVDT/encoder position feedback (±0.5° accuracy)
- Integrated monitoring displays on bridge
3. Oil Distribution (OD) Box
Critical Functions:
- Precision oil distribution to pitch control cylinders
- Hydraulic pressure regulation
- System status monitoring interface

Design Features:
- Marine-grade stainless steel (316 SS) construction
- Multi-stage sealing system:
- Mechanical seals
- O-ring assemblies
- Gland packing
- Pressure rating: 150 bar design pressure
4. Performance Characteristics
Operational Parameters:
- Pitch change rate: 2.5-3.5°/sec (5°/sec max)
- Full range transition (35° to -35°): 20-30 seconds
- Positioning accuracy: ±0.5°
Efficiency Benefits:
- Fuel savings up to 30% vs fixed-pitch propellers
- 15-20% better efficiency at partial loads
- Reduced engine wear through constant RPM operation
5. Maintenance Protocol
Preventive Maintenance Schedule:
| Interval | Activities |
|---|---|
| Daily | Visual inspection, oil level check, leak detection |
| Monthly | Filter inspection (ΔP>3 bar replacement), valve function tests |
| Annually | Complete oil change, pump servicing, sensor calibration |
| 3 Years | Hub seal replacement, mechanical overhaul |
| 5 Years | Pump rebuild, complete system reconditioning |
Common Failure Modes and Solutions:
- Slow Pitch Response
- Causes: Pump wear, clogged filters, low pressure
- Solutions: Pressure testing, filter replacement
- Oil Contamination
- Causes: Seal failure, water ingress
- Solutions: Oil analysis, seal replacement
- Position Drift
- Causes: Valve leakage, sensor drift
- Solutions: Valve reseating, sensor recalibration
6. Technical Standards Compliance
- ISO 4406: Oil cleanliness (Target 17/14/11)
- ISO 13709: Hydraulic pump requirements
- DNVGL-RU-003: Marine classification rules
- SOLAS Ch.II-1: Safety requirements
- IEC 60092: Electrical standards
7. Comparative Analysis: CPP vs FPP
| Parameter | CPP | Fixed Pitch |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Operational Flexibility | Excellent | Limited |
| Partial Load Efficiency | 85-95% | 60-75% |
| Maintenance Complexity | Higher | Lower |
| Maneuverability | Superior | Basic |
8. Special Applications
- Tugboats: Precise thrust control requirements
- Research Vessels: Dynamic positioning needs
- Passenger Ships: Vibration and noise reduction
- Naval Vessels: Tactical maneuverability
9. Emerging Technologies
- Electro-hydraulic actuators: Replacing traditional hydraulics
- AI-based predictive maintenance
- Digital twin integration for performance optimization
- Solid-state pressure sensors for improved reliability
10. Conclusion
Modern CPP systems with integrated OD boxes represent the pinnacle of marine propulsion technology, offering unmatched operational flexibility and efficiency. While requiring more sophisticated maintenance than fixed-pitch alternatives, their performance advantages make them the preferred choice for demanding marine applications. Proper fluid maintenance, regular system checks, and adherence to manufacturer specifications are essential for achieving the system’s full 25+ year service potential. Future developments in electrification and smart control systems promise to further enhance CPP capabilities in the coming decade.








